Why do airlines still make economy-class seats that recline?

It’s one of the most controversial issues in the skies. Like a baby beginning to wail at take off, or a businessman ordering one too many miniature gins, seeing the seat in front recline onto you can cause consternation.
Some passengers respond with a Mexican wave of retaliation reclines. Others simply choose obstinance – hitting the offending seat with their fist, or blasting the recliner with the air conditioner nozzle. It can be nightmarish on a long haul flight, especially if it results in your lacklustre dinner being thrown into your lap. But reclining seats remain the standard in economy class, despite their potential for passenger confrontation.
The reclining seat became common in the post-war era; essentially as soon as air travel became a commercial prospect. Until the early 2000s, almost all short haul flights were kitted out with recliners, regardless of the ticket cost, and they remain a vital part of the offering for long-haul flights, allowing customers to stretch out and – just maybe – get some sleep.
Losing the recline can save airlines money
In fact, an online poll in 2014 by Telegraph Travel garnered more than 26,000 votes, with around 70 per cent of readers in favour of banning the option to recline. Those readers will be happy to learn that in short-haul cabins, that ability to slide backwards is slowly disappearing, although not for reasons of passenger comfort – or at least not explicitly. Airlines have found that by removing the “kinematics” (the part that moves) they can save up to a kilogram of weight per seat. This in turn saves the airline on vital fuel costs. Allegiant Air has estimated that, without reclining seats, they save around 110,000 gallons (or around £281,590) of fuel each year.
It also means that there are less things to fix: gone are the troublesome mechanisms that can get jammed by an impatient passenger or stuffed with food by an errant toddler. That isn’t to say that passengers are unable to lean back. On British Airways flights shorter than four hours, seats come “pre-reclined” at a slight, unchangeable angle. Jet2 were an early adopter of this model and their seats have been the same since 2009. For Ryanair, however, the ability to recline at all was scrapped along with seatback pockets in 2004.
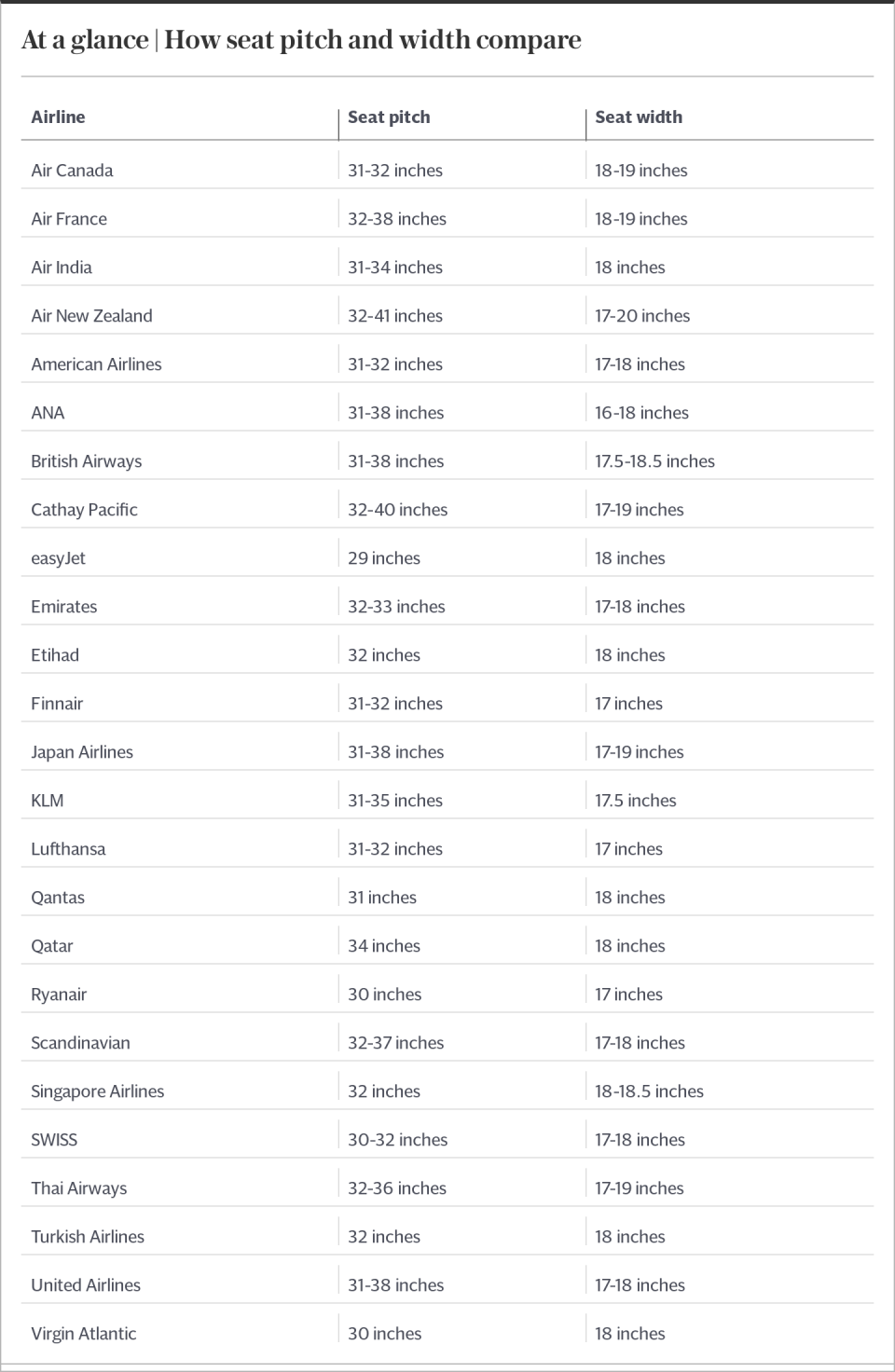
This, in itself, helps airlines save money. There are around 30 rows of seats on a standard Boeing 737 or Airbus A320 – but this can be increased if recline is removed. Take an inch off the pitch (the distance between a row of seats), and designers can squeeze in another row that can be filled with paying customers.
Airlines have mooted alternatives
Of course, another benefit is that intra-passenger disputes are less likely. Some airlines, such as Finnair, have even removed the recline option from their business class seats entirely, instead prioritising legroom and seat width.
Others, like Cathay Pacific and ANA, have experimented with using a “fixed shell” design, which allows seats to slide backwards within a sturdy, unmoving casing. Although popular with customers because the design allows for more personal space, it has nonetheless been largely discounted as an option: as ever, the heavier shells result in higher costs for the airline.
For passengers, the benefit of reclining space came as a compromise: the ability to lean back came with the sacrifice of additional leg room. Yet the ability to recline on a long-haul flight, especially a red-eye, is vital for passengers hoping to sleep. This means that some cabin designers think there will always be a place for them.
For the red-eye, recline is vital
James Lee, the Creative Director of design company Butterfly Flexible Seating Solutions in Hong Kong, told Telegraph Travel that the function remains vital. “Recline is important for sleeping comfort, so it is definitely going to stay; at least in long-haul aircraft. If it was possible, airlines would remove the option entirely – it adds so much cost. It’s only there due to passenger preference.”
Yet pitch has been steadily decreasing across most major airlines for decades. Qantas, for example, has reduced theirs from 34 inches in 1987 to 31 inches today. And as pitch decreases, the decision to recline becomes ever more controversial. As passengers have less leg room, they are more inclined to recline, making the impact on the passenger behind increasingly significant. Today, every centimetre counts.

Alejandro Núñez Vicente, an industrial designer from Madrid and CEO of Chaise Longue Economy Seat, is a recline evangelist. “It’s the minimum the airline can offer you in terms of comfort,” he says. Núñez Vicente believes that as low-cost airlines race to offer the cheapest ticket price, almost every other aspect of cabin comfort will be removed – even on long-haul flights. But the option to recline is non-negotiable.
“I believe that recline is the basic need of any passenger and if you take away that, the airline will completely disappear or won’t get any tickets sold. In this industry, we’re always talking about reducing, taking away, getting rid of, making things smaller,” he says. “It’s all to the detriment of the passenger experience, when I believe that it should be the other way around. We have more technology, so things should be getting more comfortable, not less.”
That certainly chimes with the experience of travelling on low-budget airlines in Europe. Famously, Ryanair even joked about introducing standing seats in the cabin. Even in higher-end European airlines, having a genuinely comfortable amount of space around the seat is something only available in the upper classes.
It’s something they recognise as a risk – KLM, the Dutch Airline, even tweeted that it was introducing an alarm system to alert passengers of recliners – before it was revealed as an April Fools’ Day hoax. But there are, of course, exceptions.
KLM is proud to introduce a revolutionary new cabin feature: The Recline Alert System. We've developed a sound effect that notifies passengers when the seat in front of them reclines. The new system will be introduced on all KLM flights from April 1, 2023. #KLM #comingsoon pic.twitter.com/NRapmHMVLU
— KLM (@KLM) March 31, 2023
“Emirates, Etihad, Qatar – these airlines have support from their governments, and while it might be more expensive for them, their cabins are much more comfortable.” says Núñez Vicente.
The radical reclining alternatives
Perhaps reclining seats are just a matter of etiquette. If dinner has just been served, pushing back your chair into the people behind you is rather ungenerous behaviour. If the aircraft is gliding across the Atlantic at midnight, however, that silver button should be used with gusto.
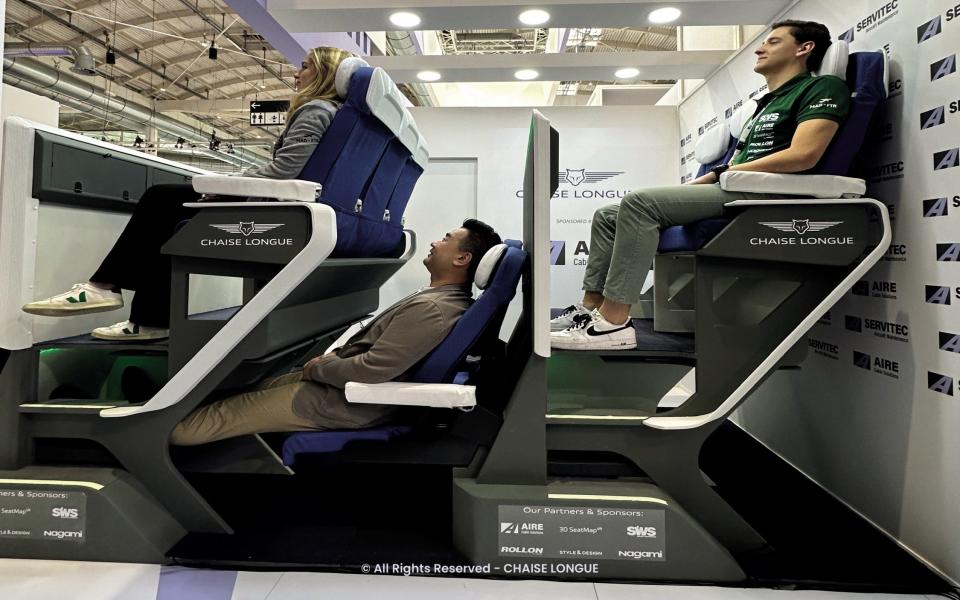


Or we can go more radical. Núñez Vicente has designed the Chaise Longue, a double-decker seating concept that allows economy-class passengers to recline without interrupting each other’s space.
Designed to slot into the central section of a wide, long-haul cabin, the stacked row allows people in the upper section to lean back into empty space – meaning those in the lower rows are unencumbered. They, in turn, can recline to their heart’s content. Feet slot into a “bucket” area, allowing customers to properly lie down. It’s a far cry from the standard BA offering.
His design did cause some consternation when renders appeared online earlier in the year, however, with many decrying it as too claustrophobic. Núñez Vicente insists that renders of any cabin would make them seem cramped. He’s keen to point out that the Chaise Longue also has space for wheelchairs, and can be adapted for either economy or business class, depending on the airline’s preference. That ability to recline without impeding others, though, might just be the winning tactic.


