The three big safety questions raised by the Cuban plane crash, 2018's latest air disaster
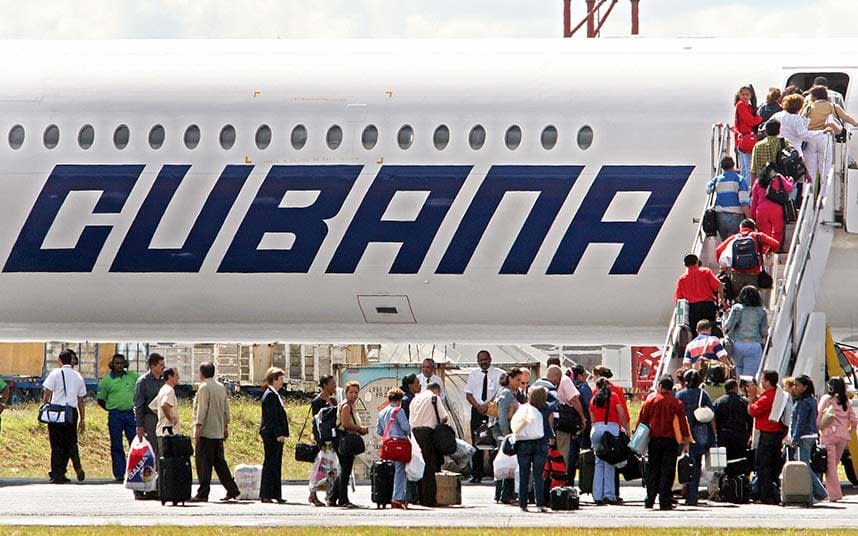

Amid the frenzied build-up to the royal wedding on Saturday, many will have missed the news that an ageing Cuban airliner carrying 113 people had crashed shortly after take-off.
Three days on and still little remains clear about what happened to the Cubana de Aviación 737, only that three passengers managed to survive but remain in a critical condition.
In the wake of the crash, Cuban authorities have announced an investigation while Mexico says it will look into the charter company that leased the state airline the aircraft.
Is it dangerous to fly in Cuba?
The crash of the domestic flight appears to have international links, with Mexico-based Damojh Airlines, also known as Global Air, leasing the Boeing plane to the Cuban flag carrier. Over the weekend it emerged that Guyana had banned the same aircraft from its airspace after its civil aviation body said it became aware that crew were allegedly overloading it with luggage on flights to Cuba.
A retired pilot from Cubana wrote on Facebook that it had rented another aircraft from the company, which dropped off radar (but later landed safely) for unknown reasons eight years ago. A pilot who used to work for Damojh told Mexican newspaper Milenio that he had previously complained about inadequate maintenance of aircraft. The company is yet to comment on the allegations.

However, Cuba’s own air travel history is not free from tragedy. According to the Aviation Safety Network (ASN), which records all air crashes and incidents reported around the world, there have been 51 recorded accidents involving the country’s state airline Cubana, including the 1998 crash of a Tupolev Tu-154 that resulted in the deaths of 80 people.
Of air travel in the Caribbean country, the Foreign Office warns of “concerns about standards of maintenance of public transport”. However, it does point readers in the direction of an International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) audit that lists Cubana as safe.
Though the plane involved in the crash was a leased US-made Boeing, much of Cubana's own 14-strong fleet of aircraft are Russian-made Antonovs or Tupolevs. Such is the concern surrounding flight safety in Russia that, Airline Ratings, one of the world’s leading authorities on measuring airline safety, automatically marks a carrier down if they use only Russian-built aircraft.
David Gleave, an aviation safety investigator, said that many factors could have come into play with regards to Friday’s crash but added: “You would expect Cuba to have a relatively high probability of an accident”.
He continued: “You will always have problems where there are massive commercial pressures. If Cubana wanted to hire more modern airplanes it probably could but it would be more expensive. What were the trade sanctions in force at the time when the decision to hire that plane was made?”
He said that airlines “under pressure to go rather than stop” - in terms of keeping their operations running because of costs - might be more likely to experience safety incidents.
Two crashes this year - one in Russia in February and another in Iran in March, more on which below - both raised issues about airlines failing to run proper maintenance programmes.
Cuba does not feature in the ASN’s top 25 “worst geographical regions” for civil airliner accidents. However, that is measured only by number of fatal accidents so does not take into account total flights operated.
Are older planes less safe?
The age of the aircraft involved in last week’s crash has been highlighted. The 737, registered XA-UHZ, left the Boeing factory almost 40 years ago. It was delivered to Piedmont Airlines, a Maryland carrier that currently flies under the American Eagle brand, in 1979, before spending time in the fleets of US Airways, Royal Airlines (now defunct), Canada 3000 (defunct), the US Navy, Magnicharters and Avolar Aerolineas (both based in Mexico) and Honduran carrier EasySky Airlines. It had been in Global Air’s fleet since 2014.
But are older planes really more likely to go wrong? Patrick Smith, a US pilot and author of Cockpit Confidential, claims that as planes get older they come under ever greater scrutiny. “Inspection criteria grow increasingly strict,” he said. “Commercial aircraft are built to last more or less indefinitely, which is one of the reasons why they’re so expensive - it’s common for a jet to remain in service for 25 years or more.”

Nevertheless, it is uncommon for an airline to possess planes that have been in service for as many as 40 years. Research by Telegraph Travel last year found that the oldest plane used by a UK airline was a 31-year-old 737, registration G-CELH, owned by Jet2.com. The BA fleet has an average age of 13 years, while its oldest aircraft is a 747, registration G-BNLK, which it received in 1990. Ryanair’s fleet has an average age of just 6.5 years.
More important than the maturity of the plane is how well it is maintained, argues David Gleave, but he also says the crash rate of the majority of planes gets worse with age.
“Statistically speaking, if you’re going to fly a 40-year-old plane around the developing world then the risk is going to be higher,” he said.

Why have there been so many crashes in 2018?
As Telegraph Travel reported in January, 2017 was - by some distance - the safest year in aviation history. According to the ASN there were just 10 fatal accidents involving commercial flights last year, resulting in 44 deaths. This was down from 16 fatal accidents and 303 deaths in 2016. Furthermore, none of those fatalities involved a passenger jet.
This year, however, we’ve already seen four major disasters. On February 11, Saratov Airlines Flight 703 crashed after leaving Moscow with all 71 on board perishing. One week later 66 people died when Iran Aseman Airlines Flight 3704 went down near the city of Yasul. US-Bangla Airlines Flight 211 crashed near Kathmandu on March 12, resulting in 51 deaths. There was also a harrowing incident on a Southwest flight, where a window was smashed and a female passenger killed.
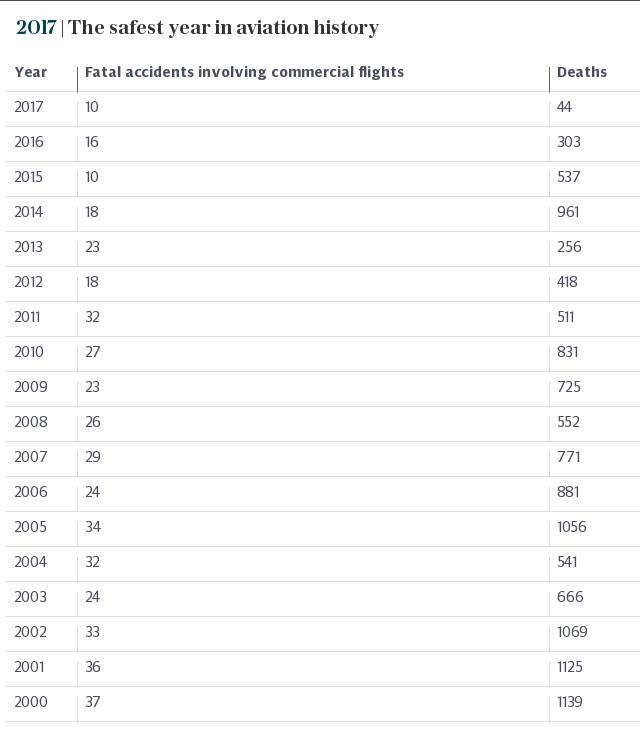
ASN’s database shows 301 deaths involving commercial flights so far this year (as of May 21), almost seven times more than the whole of 2017. Should this rate continue until the end of 2018, it would mean more than 700 deaths, making it the deadliest year since 2014 (when 18 accidents involving commercial flights saw 961 perish, the two Malaysia Airlines crashes being the most high profile).
But this would still be way down on the numbers of annual fatalities seen in previous decades. More than 1,000 deaths per calendar year was commonplace until just over a decade ago. In 2005 there were 1,056. The figure for 1996 was 1,924. The deadliest year of all time was 1972, when 2,469 people died in 55 accidents involving commercial flights - a number that's all the more remarkable when you consider how few departures there were compared with today (around 9.5 million, compared with almost 37 million in 2017). A total of 11 crashes saw at least 100 perish in 1972, including four Aeroflot flights, and others involving Iberia, Sterling Airways, Alitalia, British European Airways, Interflug, Spantax and Eastern Air Lines.
Modern air travel remains remarkably safe. Over the past five years, the fatal accident rate has ranged from around one for every 7.5 million departures (2017) to one for every 1.5 million departures (2013).
“Last year was effectively a lovely statistical blip,” said David Gleave. “We are a long way from having solved all the problems [with flying], but it is getting safer and there remains a downward trend in the per flight probability [of a crash].”

